ISO 27001 certification
- An ISO 27001 certification can speed up your sales cycle and boost customer trust
- The larger your company, the more complex it gets to become certified
- In this guide we go over every detail you should know before you start


Getting an ISO 27001 certification is the best indicator to suppliers, customers, and stakeholders that you take information security seriously. It’s also a great starting point to set up a robust cybersecurity strategy.
No matter if you’re an SMB or a large-scale corporate, this guide pulls together the most relevant information in one place.
ISO 27001 sets the global standard for an information security management system (ISMS) that helps you establish a framework for keeping information secure. In 2022, the ISO 27001:2013 version was updated to its latest version, ISO 27001:2022.
An ISMS creates a set of rules and processes that help mitigate the damage of a cyber or ransomware attack as well as a security breach, which, nowadays, needs to be on every company's agenda.
The stats speak for themselves: During the third quarter of 2022, a staggering 108.9 million accounts fell victim to breaches, marking a substantial 70% surge compared to the preceding quarter.
Using an ISO 27001-compliant ISMS lets you easily and affordably manage the security of your organization's data. Plus, it makes your customers, investors, and other important stakeholders feel confident that you're following the best global practices for keeping information safe.

In order to be able to play the desired video, you agree that a connection to the servers of YouTube, LLC, 901 Cherry Ave, San Bruno, CA 94066, USA is established. This transmits personal data (device and browser information (in particular the IP address and operating system) to the operator of the portal for usage analysis.
You can find more information about the handling of your personal data in our privacy policy.
The ISO 27001 certification is granted when you meet the requirements of the ISO 27001 standard. Once you've established your ISMS, an independent accredited certification body conducts an audit and issues a certificate upon successful completion. A certification body is basically an independent institution that can certify companies with the ISO 27001 certificate after successfully passing an external audit.
The certification essentially proves you have taken the appropriate steps to protect your most valuable information. This includes intellectual property, trade secrets, proprietary data, and other valuable assets. While the specific term "intellectual property" may not be used, the principles of information security within the ISO 27000 series standards are designed to encompass various forms of valuable and sensitive information, including intellectual property.

In order to be able to play the desired video, you agree that a connection to the servers of YouTube, LLC, 901 Cherry Ave, San Bruno, CA 94066, USA is established. This transmits personal data (device and browser information (in particular the IP address and operating system) to the operator of the portal for usage analysis.
You can find more information about the handling of your personal data in our privacy policy.
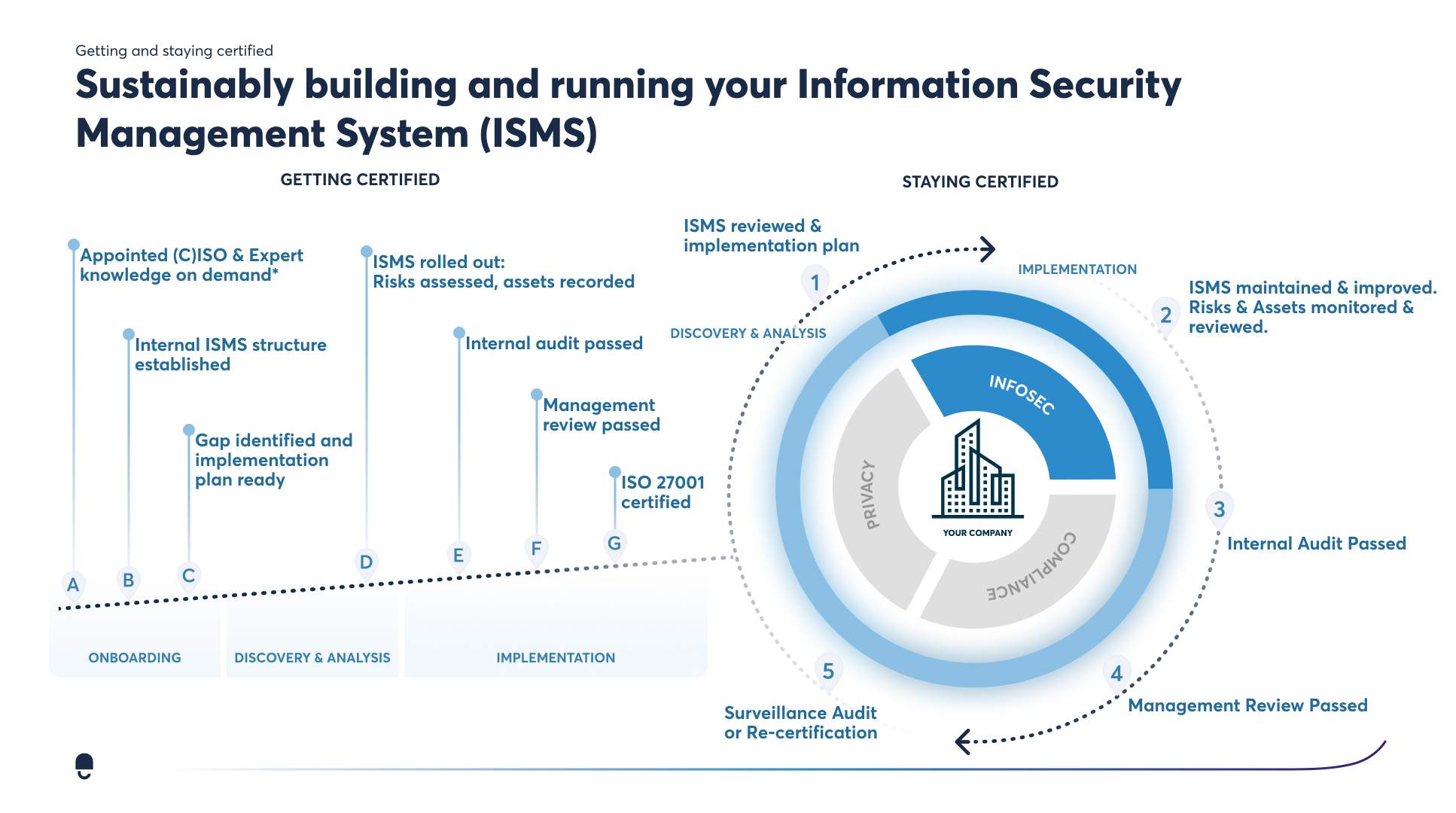
Establishing and implementing an ISMS, in its simplest form, can be broken down into 4 phases, also known as the PDCA cycle:

The certification is beneficial for a number of reasons. These are the most important ones:
Establishes stakeholder trust
Having an ISO 27001 certificate demonstrates your dedication to safeguarding information and underscores your business's credibility in partners' eyes. This can give you a competitive edge and enhance your brand reputation.
Assists legal compliance
ISO 27001 certification aids in meeting your various business, legal, financial, and regulatory commitments. You can mitigate the likelihood of costly breaches, subsequently reducing the risk of expensive legal consequences and fines.
Secures personal data and intellectual property
The ISO 27001 certification process offers an impartial evaluation of your information security strategy. It could also assist in managing your intellectual property and data sources while creating tangible proof of implementation.
Mitigates costly cyber-related data breaches
Data breaches come with a hefty price tag. In 2023, the average cost of a data breachwas estimated at around $4.45 million (IBM, 2023). The ISO 27001 certification safeguards your information through established procedures and processes, helping you avoid such financial burdens.
Sets the foundation for reducing risk
Risk management is important to keep your business operations running and should be carried out continuously. Yet, setting up a risk management structure from scratch can be immensely time-consuming. ISO 27001 gives you a framework to define the criteria of risk management in your company.
The ISO 27001 certification is relevant for pretty much any business dealing with information and data. It’s not mandatory, yet it’s common practice and often a prerequisite for many business stakeholders. This is because doing business with you without relevant policies and procedures to manage risks could put their information and data at risk.
Industries particularly affected by ransomware and cyberattacks and where ISO 27001 certification is becoming the norm include:
Yet, with the current upward trend of cyber criminality, all businesses—from SMBs to large-scale corporates—need to consider information security. And getting ISO 27001 certified is a clear roadmap to making it a priority.
Getting ISO 27001 isn't easy by default. It does come with its complexities, especially when plenty of stakeholders and complicated processes become involved.
Furthermore, ISO 27001 certification is usually a top-down decision, which means that top management must be involved sooner or later. As a business, you should ensure that you have the right experience within the team to convince decision-makers about the certification and to navigate the whole process.
Here are four tips for a successful ISO 27001 certification:

In order to be able to play the desired video, you agree that a connection to the servers of YouTube, LLC, 901 Cherry Ave, San Bruno, CA 94066, USA is established. This transmits personal data (device and browser information (in particular the IP address and operating system) to the operator of the portal for usage analysis.
You can find more information about the handling of your personal data in our privacy policy.
Since the ISO 27001 standard is designed to be customizable to your organization, there are several instances where businesses could go wrong in their implementation process.
Based on our extensive experience of working with varied clients, we’ve pulled together a list of the most common pitfalls businesses face when implementing the standard, along with advice on what you can do to avoid them.
Not defining the right scope
Finding the right scope for implementing your organization’s ISMS can be tricky. Organizations often set overambitious implementation goals, leading to the adoption of several redundant and unneeded controls and processes.
This can lead to resource wastage, increased cost of information security, and demotivated employees chasing unachievable targets.
On the other hand, an organization may define their scope too narrowly, ignoring controls that are absolutely necessary. This could lead to noncompliance with the ISO 27001 standard and can make it appear that your organization is not in control of its ISMS during the certification audit.
Lack of management
Implementing ISO 27001 controls is often considered to be an IT exercise and the responsibility of the IT department. In reality, it is a management standard for information security. The upper management in an organization may not see the value the implementation of ISO 27001 adds to the business, and they may be hesitant to fully commit.
Too few resources
Often, ISO 27001 implementation falls to a particular individual or team within the organization. This type of approach can create information security silos where only very few individuals are aware of the controls and procedures around the ISMS and other aspects of the standard. The loss of such individuals could cause the collapse of the entire ISMS.
Find out which two other mistakes are common for all businesses and how you can prevent them from happening in our free guide about the most common pitfalls during ISO 27001 certification.
Usually, the process can take 6 to 12 months, depending on business size and complexity. The use of designated solutions like the DataGuard platform can speed up the process to as little as 3 months (also depending on a business’ unique circumstances).
First steps are called the ramp-up phase, where the main chunk of work is done. You carry out a gap analysis that aims to close up to 50% of your company's most significant risks in as little as 8 weeks.
Getting through the process involves:

The ISO 27001 certification needs to be renewed every 3 years. We recommend remaining compliant to protect your company’s assets and ensure your information remains safe. Furthermore, companies must pass the annual surveillance audit to verify compliance and to avoid expiry of the certification before the three-year cycle.
If you already comply with the ISO 27001:2013 certification, you don’t necessarily need a separate audit to transition to the new revision. You can either undergo a standalone transition audit or you can opt for a transition audit at the time of annual surveillance or re-certification. This depends on where you are in the certification lifecycle.
Here is an overview of a typical transition roadmap:

Complying with the new 2022 standard is bound to save your organization resources and frustrations. This is why we recommend transitioning sooner rather than later. You can gain detailed insights here: DataGuard's expert insights on the ISO 27001:2022 update.
The benefits of implementing ISO 27001 are plenty—both for your business and external parties and stakeholders. Here's an overview of the most important ones:
If you’re looking to establish an information security management system, ISO 27001 is the ultimate baseline that will cover most businesses' compliance and information security needs. However, you may find yourself in scope of the EU's new NIS2 regulations, which have additional requirements.
What your customers and suppliers require will depend on where your business operates. ISO 27001 is an internationally recognised standard known as the gold standard, regardless of geographic location or industry. If you are unsure, why not have an initial consultation with an information security expert?

In order to be able to play the desired video, you agree that a connection to the servers of YouTube, LLC, 901 Cherry Ave, San Bruno, CA 94066, USA is established. This transmits personal data (device and browser information (in particular the IP address and operating system) to the operator of the portal for usage analysis.
You can find more information about the handling of your personal data in our privacy policy.
Accredited vs. non-accredited certification
As we have learned so far, ISO 27001 certification is not mandatory for businesses. However, it’s recommended to be compliant with the standard. But what’s the difference between being certified and being compliant? In general, you must understand the three ways of communicating the implementation of ISO 27001:
The difference is that an independent third certification body validates an accredited certification. A non-accredited certification means you have implemented the ISO standards but have not undergone an external audit, nor have you been issued a certificate for an external certified body.
Often, certain contractual agreements require an official accredited certification. Apart from this, achieving an accredited certification is highly recommended. You can use it in your communications towards customers and have an external assess your information security to ensure your ISMS is in check.
We strongly recommend seeking certification exclusively through accredited bodies. Business partners often do not acknowledge certifications lacking confirmation from an international accreditation body. Read more about accredited bodies here.
Identify gaps and kick off ISO 27001 implementation
Run a gap analysis and, with our experts, create a tailored plan that defines your ISMS scope and implementation path.
Build your ISMS
An ISMS is a set of policies and controls that strengthen your organization’s information security.
Identify and manage risks
Brainstorm potential scenarios, evaluate their financial, reputational, legal, and operational impact, then apply technical or procedural measures to mitigate them.
Protect information assets
Document all assets (hardware, data, personnel), categorize them by criticality and value, and assign ownership and responsibilities for their protection.
Pass your ISO 27001 audit
An accredited auditor reviews your ISMS for ISO 27001 compliance. DataGuard experts support you with a thorough internal audit to maximise your chances of success.
The real journey begins: Maintaining your ISMS
Regularly review and update your ISMS with risk assessments, audits, and training. Pass annual surveillance and 3-year re-audits to stay certified and continuously improve.
Conducting a risk assessment is not as straightforward as one might think. First of all, there are many different approaches to risk assessments. It’s not necessarily common practice, but scenario-based is the most effective way to access risk. This means considering past occurrences and analyzing risky scenarios that may cause an issue.
The risk assessment consists of the following:
A platform like DataGuard can help move you through risk assessments in an efficient way with a tested and proven process. Check out the full article on conducting ISO 27001 risk assessment in 7 steps.
An integral part of your information security program is the risk treatment plan. This plan is all-encompassing and is meant to execute measures to either accept, avoid, transfer, or mitigate the possibility or consequences of risks.
Of utmost importance within a risk treatment plan is the aspect of implementation. Its significance lies in guaranteeing the actual execution of risk treatment procedures.
You can read ISO 27001 risk treatment plan: How to develop the right one here.
Documentation is the basis of your ISMS and the most important part of getting and maintaining your certification. If it's not documented, it's not relevant.
You need to keep track of many things when it comes to documentation. To give you a complete overview of the documentation required for ISO 27001 certification, along with information on preparing said documentation, we have created a detailed list:
Definition of the scope of application of the ISMS (Information Security Management System)
The scope of application of the ISMS is defined in the so-called “Scope Document.” This determines which divisions of your company are subject to the ISMS. Your ISMS doesn’t necessarily need to be rolled out across the entire company—only the relevant departments and divisions. That said, in the case of smaller companies, it will usually cover all departments.
%20.webp?width=1599&height=400&name=Definition%20of%20the%20scope%20of%20application%20of%20the%20ISMS%20(Information%20Security%20Management%20System)%20.webp)
Coordination and documentation of the guideline on information security
The objectives which your company seeks to achieve with your ISMS should be clearly defined in the guideline on information security. This document should also demonstrate why information security is a top priority in your organization and that management is responsible for the guideline.
This does not have to be formulated by management themselves but must always be approved by the necessary stakeholders. The ISO standard already specifies the following information security objectives:

Definition of risk assessment and risk management methods
You will need to identify your company’s risks, assess them individually, and define an appropriate methodology for risk management. The assessment should always be carried out by the respective risk owner and should ultimately be approved by management.
In addition, this area should be coordinated within the company, ideally with your ISO, CISO, or risk management department. Given that this process must be repeated on a regular basis, it can result in a lot of effort, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises that lack in-house security and risk experts. Repetitions happen when there are new assets in the company that require a risk assessment.

Preparing a declaration of applicability
As part of this step the ISO/CISO shall agree, with the respective specialist departments, which of the 93 controls stated in Appendix A of ISO 27001:2022 must be carried out or which are relevant for the company.
ISO 27001 has specified various areas such as cryptography, HR security, or operational security. Companies may exclude some of these areas by providing appropriate justification. For example, if a business does not have a loading zone, it is simply not necessary to draw up rules for loading zones.

If you choose to work with experts such as DataGuard or an external consultant, you may receive documentation templates that will cut down your manual work significantly compared to creating them from scratch.
An audit is basically the process of checking that your ISMS meets the requirements and criteria of a standard. If you are certifying against ISO 27001, it will be the requirements of the ISO 27001 standard.
Audits ensure the success of your ISMS by identifying information security non-conformities and can be either internal or external. Internal audits can be carried out using the organizations’ own resources—whether that’s internal company employees or contracted independent consultants.
External audits are carried out by a certification body, external partners, or customers who want to assess the ISMS on their own terms. The latter is the exception than the rule—when referring to an external audit, a certification body is meant in most cases.
Audits are incredibly important because they are:

External Content: YouTube Video
In order to be able to play the desired video, you agree that a connection to the servers of YouTube, LLC, 901 Cherry Ave, San Bruno, CA 94066, USA is established. This transmits personal data (device and browser information (in particular the IP address and operating system) to the operator of the portal for usage analysis.
You can find more information about the handling of your personal data in our privacy policy.
Internal audits are vital for long-term success in earning and keeping your ISO 27001 certification. They should be carried out on a regular basis by employees within the company, as opposed to external auditors coming into your company to assess your ISMS.
However, independence and qualification are a must for being an internal auditor. Another option is to perform internal audits with external consultants, like the experts at DataGuard, who also offer regular audits. Internal audits are your best bet for catching gaps in your documentation and improving it.
When you are getting certified for the first time, the internal audit ensures you have everything you need in place to pass your certification on the first try.
An internal audit checklist will help you keep an overview of the necessary steps. Here is an overview:
Get a full breakdown of how to conduct an internal audit.
You will be in touch with your auditor before the external audit takes place to agree on resources and timelines.
In general, there are four types of external audits:
To do this, the audit will focus on:
Once you have completed Stage 2 and passed the audit, you will receive your official certification.
Depending on the size of your company, you can be audit-ready in about 8 weeks. If you decide to go the manual route of building your documentation from scratch, it can take at least 4 months.
It is also important to take into account several other variables that may affect the time it takes for you to obtain the certification.
When implementing your ISMS, you may experience unforeseen challenges which may delay certification as well.
The external auditor will usually give you an indication during your audit whether you are likely to pass or fail. Major nonconformities may lead to a failed external audit. Although this might seem like a major setback, it needs to be seen as an opportunity to improve.
When it comes to the 2022 version of ISO 27001, there are 93 Annex A controls that cover various areas of an organization. These controls are segmented into 4 different categories (domains). Depending on which are relevant for your operations, risks, industry, and customers, you will fulfil the requirements in specific annexes.
You will receive an audit report; this will be your go-to to identify what you need to change in order to pass your next external audit. It is also recommended to speak with the auditors for further clarification on what precisely needs to be improved.
In general, non-conformities are classed as:
There is no direct penalty for not passing an external audit, but not achieving certification may result in improper risk management, reputational damages, and additional financial costs. Preparing thoroughly and undergoing internal audits significantly reduces the risk of failing. If you happen to have failed an audit in the past, we recommend the following:

The main requirements when it comes to the ISO 27001 certification are: documentation, undergoing audits and ensuring your employees adopt the processes.
Documentation includes the creation and maintenance of necessary documentation for your Information Security Management System (ISMS), such as policies, procedures, risk assessments, and controls.
Undergoing audits includes both the Stage 1 Audit, which reviews documentation and readiness, and the Stage 2 Audit, which assesses the practical implementation of your ISMS. Successful completion of these audits is necessary to achieve ISO 27001 certification. You will also be required to undergo internal audits and management reviews.
It's also crucial to communicate the processes effectively This is to ensure that your organization's information security practices align with the ISO 27001 standards. You will need to have the documentation in place but also put the processes into action by ensuring employees are aware of and follow them.

In order to be able to play the desired video, you agree that a connection to the servers of YouTube, LLC, 901 Cherry Ave, San Bruno, CA 94066, USA is established. This transmits personal data (device and browser information (in particular the IP address and operating system) to the operator of the portal for usage analysis.
You can find more information about the handling of your personal data in our privacy policy.
The mandatory documents required for the ISO 27001 standard are listed below. All criteria must be followed and documented accordingly for an organization to present during external audits. The standard requires you to undergo an internal audit before an external one. This will expose any gaps in your ISMS.
Once you have prepared the documentation and undergone an internal audit as well as a management review, you need to undergo an external audit by a certified body such as the UKAS.
The price or costs for getting ISO 27001 certified depends on many things. These are the most relevant influences on what you will need to invest in your ISO 27001 certification:
This is why we cannot provide a one-size-fits-all answer, but we can give indications that will help establish a budget.
The cost of getting certified can be broken down into three phases: implementation (of your ISMS), internal auditing, and certification.
Internal costs
These costs can include:
External costs
This generally refers to the auditor's cost; on average, the cost of auditing per day is £1000 — the number of days and whether you will have a remote or on-site audit will impact external costs.
According to Statista, the global average cost per data breach is USD 4.35 million as of 2022. From a purely financial perspective, if that's a hit your company or organization can easily take, getting ISO certified might not be worth it. But you are likely to incur additional costs later on in lost business and difficulties getting new customers.
Information security is bound to become more and more important and simply shouldn't be ignored. As ransomware and cyberattacks rise year after year, companies realise that a preventive approach might be better than cleaning up the reputational and financial mess once something does happen.
Of course, you will need to take your unique ROI of getting ISO 27001 certified into account. Speaking with an information security expert can give you an idea of what you can expect cost-wise and whether it's worth investing in.
At the same time, how you go about getting certified—e.g., using a process-driven platform backed by experts or hiring a compliance manager in-house—will have a significant impact on just how much you need to invest and whether it will be worth it in the long run.
As you can see, there are plenty of aspects you need to think about when it comes to achieving ISO 27001 certification. But the best time to get started is now. Let your ISMS grow and scale with you.
The recommended and common practice to start your ISO 27001 journey is to:
The ISO 27001:2022 edition stands as the most recent iteration of ISO 27001, the global benchmark for information security management systems that you must adhere to to receive your certification. If you’re already certified and need to transition to the 2022 iteration, then our ISO 27001:2022 transition guide is your go-to resource.
An information security management system (ISMS) provides a framework of documented policies, procedures, and controls designed to mitigate information security risks. Once you’ve built your ISMS, getting it certified against an international standard such as ISO 27001 is best practice.
A control is a measure that manages risk.
When it comes to the 2022 version of ISO 27001, there are 93 Annex A controls that cover various areas of an organisation. These controls are segmented into 4 different categories (domains). Depending on which are relevant for your company, risks, industry and customers — you will fulfil the requirements in specific annexes.
Standard controls include:
Want more details on controls and their implementation? Take a deep dive here: ISO 27001 Annex A controls - A detailed guide.
An auditor will come to your company premises, review your ISMS, and speak with your employees.
Here’s the overall process:
1. Document check
First, the external auditor will review all of your ISMS-related documentation. It has now also become the norm that auditors can do this remotely. But in fact, inviting them to physically come into your company so they can get to know your team builds trust early on.
2. On-site audit
In the second step, an on-site inspection is carried out. Some of your employees will be interviewed, and your systems will also be randomly checked. In addition to employees such as your CISO/ISB, who directly deal with the ISMS, your CFO or CEO should give the auditor confidence that the financial resources for operating the ISMS are firmly set up.
You will already know during the inspection whether you’re going to pass the audit and receive the certification, as the auditor will directly address minor and perhaps even significant issues.
Afterwards, the certification body first has to prove all non-conformities addressed by the auditor, which usually gives you the chance to improve your documentation before an official result of the audit is confirmed..
Major non-conformance will lead to a failed audit. The only thing left is to set the date and conditions for a follow-up audit together.
3. Audit Report and ISO 27001 Certificate
Finally, you will receive an audit report and the certificate from your auditor. Many certification companies are currently busy, so this may take a few months.
TISAX® is a registered trademark of the ENX Association. DataGuard is not affiliated with the ENX Association. We provide Software-as-a-Service and support for the assessment on TISAX® only. The ENX Association does not take any responsibility for any content shown on DataGuard's website.
All data provided is for information only, based on internal estimates. This information is not indicative of KPIs, and is not given with any warranties or guarantees, expressly stated or implied in relation to accuracy and reliability.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@graph": [
{
"@type": "Organization",
"@id": "www.dataguard.com#organization",
"name": "DataGuard",
"legalName": "DataCo GmbH",
"description": "DataGuard, the European leader in security and compliance software, is trusted by more than 4,000 organizations across 50+ countries. We help you identify and manage your security and compliance risks and fast-track your certifications and compliance by combining expert consultancy with AI-powered automation. Our purpose-built, all-in-one platform is developed with the experience of over 1.5 million total hours by a team of certified security and compliance experts.",
"foundingDate": "2018",
"taxID": "DE315880213",
"logo": "https://7759810.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/7759810/DataGuardLogo.svg",
"url": "www.dataguard.com",
"email": "info@dataguard.de",
"telephone": "+49 89 452459 900",
"address": {
"@type": "PostalAddress",
"streetAddress": "Sandstrasse 33",
"addressLocality": "Munich",
"addressRegion": "Bavaria",
"postalCode": "80335",
"addressCountry": "Germany"
},
"sameAs": [
"https://www.linkedin.com/company/dataguard1/",
"https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEQzPZ6sCBCj9cAoBvaLL6w",
"https://x.com/i/flow/login?redirect_after_login=%2FDataGuard_dg"
]
}
]
}✅ Organization schema markup for "DataGuard" has been injected into the document head.