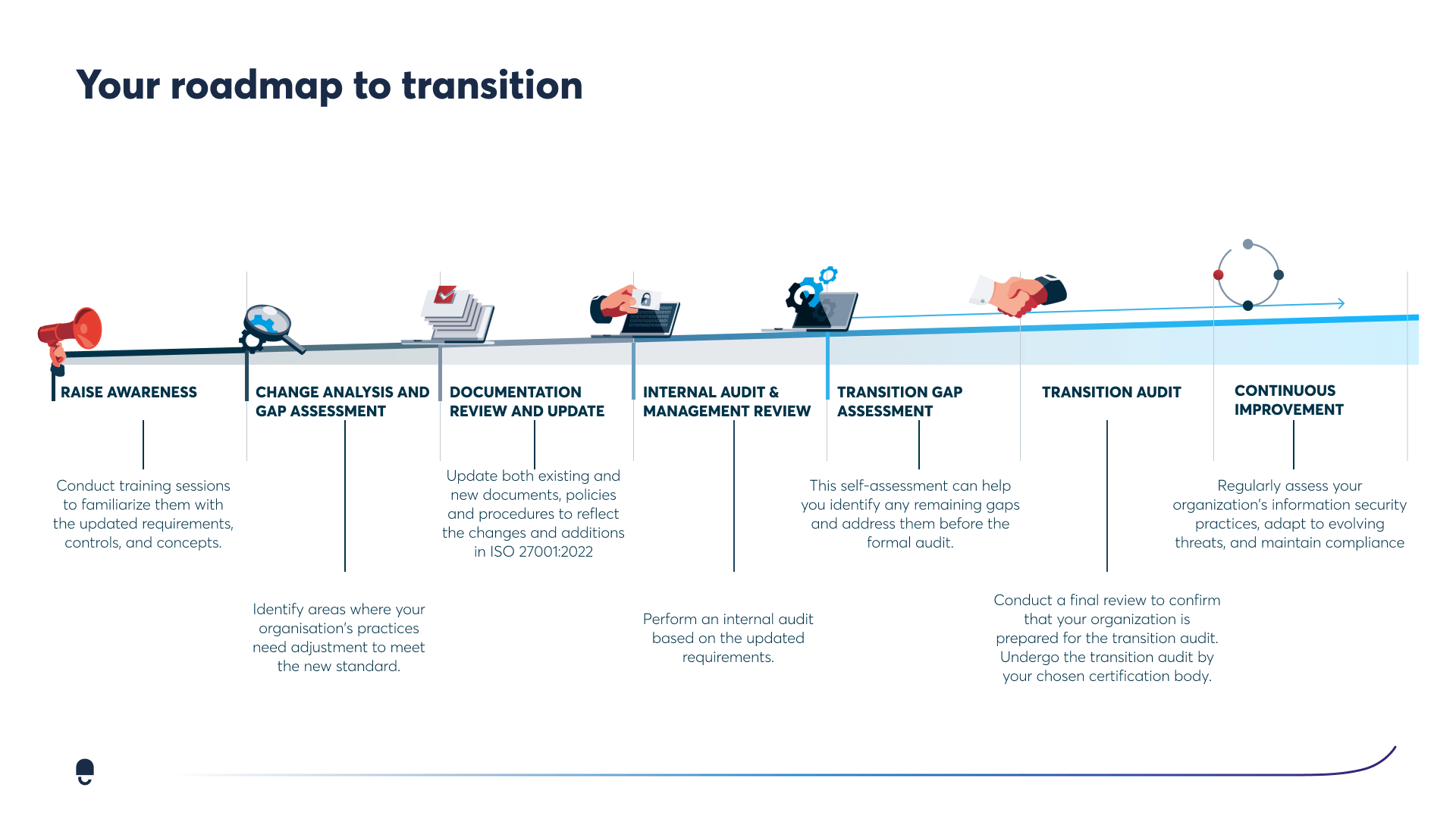
How to transition to ISO 27001:2022
This guide explores the key changes in the new ISO 27001:2022 standard and how these updates can benefit organizations. Check out the roadmap for transitioning to ISO 27001:2022, along with tips for maximizing the benefits of the transition.